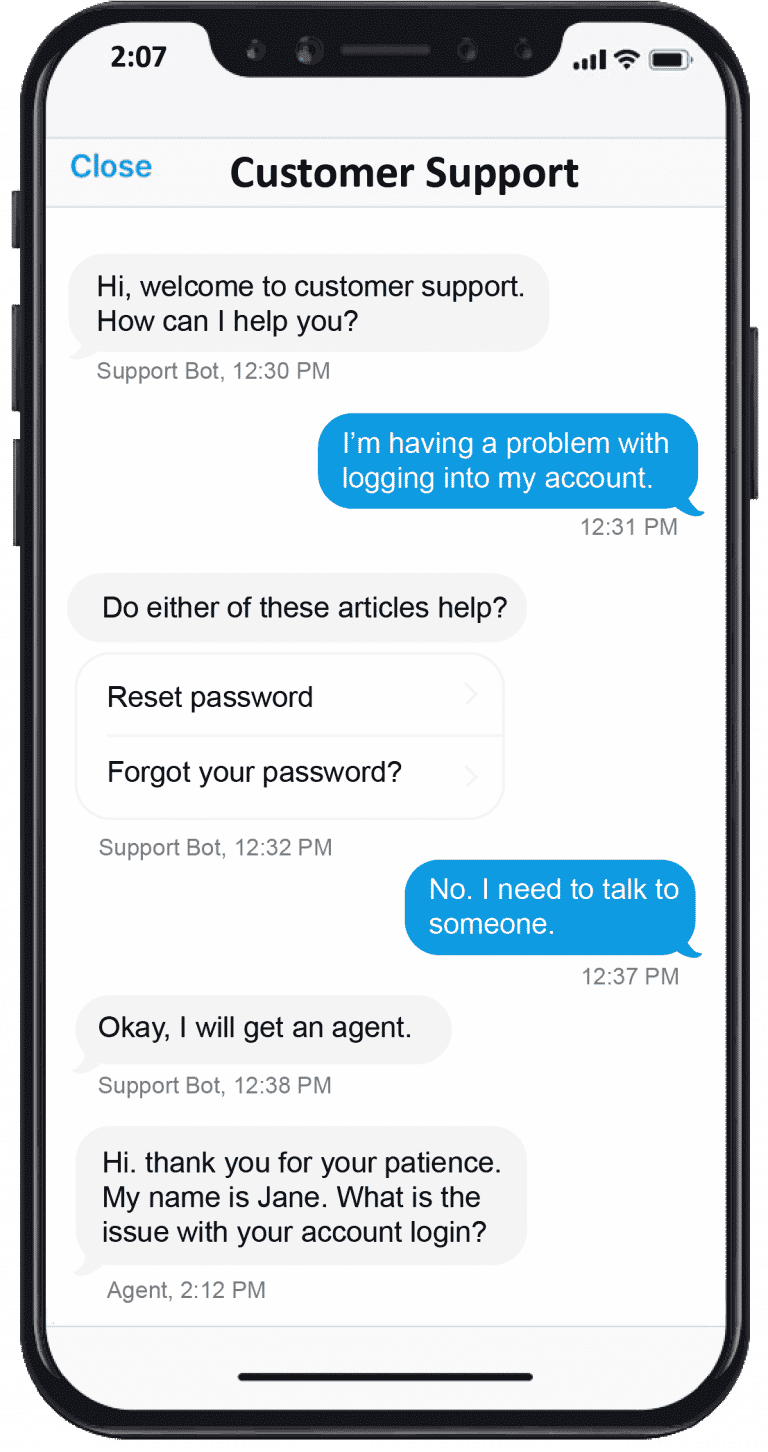
Asynchronous messaging, sometimes called “async messaging”, refers to people using messaging platforms to contact each other without both parties needing to be concurrently active in the conversation. Rather than waiting for an immediate response, a user can send a message and then continue with other unrelated tasks, while the responder can reply at a time that is convenient for him or her. Though some users may not immediately recognize this practice by its formal name, many individuals use it in the form of texting, emailing, and sending messages through Facebook Messenger and WhatsApp.
Why Asynchronous Messaging is Preferable in Customer Service
Traditional ways of contacting customer service — such as phone calls, emails, and live chat — are not suited for the modern world. People are spending less time on their computers, and more time on their mobile phones. This preference for mobile phones means that consumers prefer to be mobile; they do not want to wait by their computer for a message in a chat window. With async messaging, users can send a message from their mobile device, and then continue with other tasks while waiting for a response. Because this form of communication does not need to be conducted in real time, it likewise eliminates the expectation that customers will be helped immediately. This is unlike live chat or phone calls that imply immediate assistance, but in reality can require customers to wait for an unspecified amount of time.
Async messaging also reduces redundancy because the chat history is saved within the ticket. Synchronous communication such as live chat may initially seem best practice, but can be very inconvenient since the conversation is session-based and messages are deleted after the interaction. This requires customers to repeat their information the next time they contact customer service, and may also require them to restate their previous issues. Asynchronous messaging eliminates this inefficient repetition, allowing agents to gather customer information faster and solve the issue that much sooner.
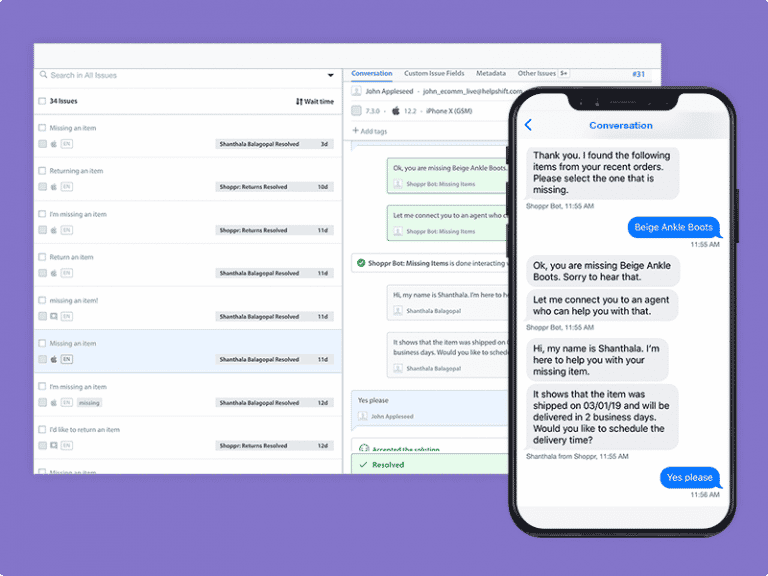
How Helpshift Supports Asynchronous Messaging
Helpshift’s AI-powered messaging platform not only allows agents to have chats with multiple customers simultaneously, but the platform capabilities also allow for bot-based information gathering and self-service. These bots can perform rote and routine tasks such as: asking for customer information, walking customers through workflows towards a resolution, and suggesting relevant FAQs. If the customer issue has not been solved by the bot, then AI-powered issue classification can categorize the issue and refer it to the appropriate agent. By deploying bots that initially respond to customer inquiries, customers have access to immediate service, and agents have more time to respond without their customers needing to wait on hold. By completing these tasks, bots save agents time that they can dedicate to more complex inquiries.
Conclusion
We know that asynchronous messaging opens up communication paths that don’t require both parties to be present at the same time but how does this improve customer satisfaction?
- Consumers can be mobile
- Reduces redundancy
- Faster information gathering
- Eliminates repetition
